The standard guide in the u s the asce 7 05 lists weights and stresses for all building materials expressed in pounds per square foot.
Miscellaneous architectural roof loads.
The north zone middle zone and the south zone are identified on the roof load zone map above.
Calculate loads on the roof assembly in accordance with asce 7 or the local building code whichever procedure results in the highest loads.
These loads shall be applicable for the design of buildings.
In order to stay intact and in place a roof must be able to resist loads both permanent and temporary that are pushing.
Specify purchase a metal roof system that has sufficient uplift resist resistance to meet the design uplift loads.
However if the attic is intended for storage the attic live load or some portion should also be considered for the design of.
Created by wind pressures.
This roof system also has wind bracing at the end trusses blocking at the supports and minor wiring.
This downward imposed load on the home is also known as the snow load.
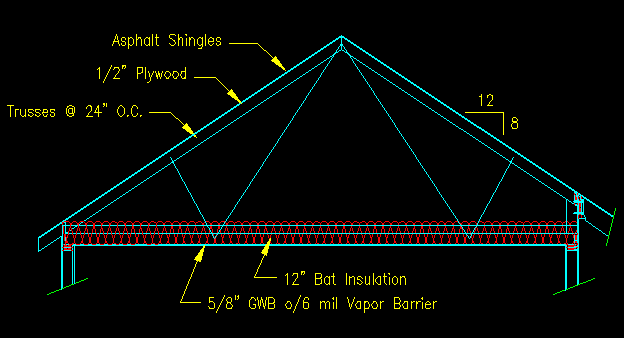
Table 3 2 2 roof system dead load.
Also the roof sheathing working in conjunction with the roof framing must function as a diaphragm to transfer lateral loads to the building s shear walls.
The roof sheathing supports gravity loads such as the roof live load snow load and vertical uplift loads.
Roof loads are a downward vertical force on the home.
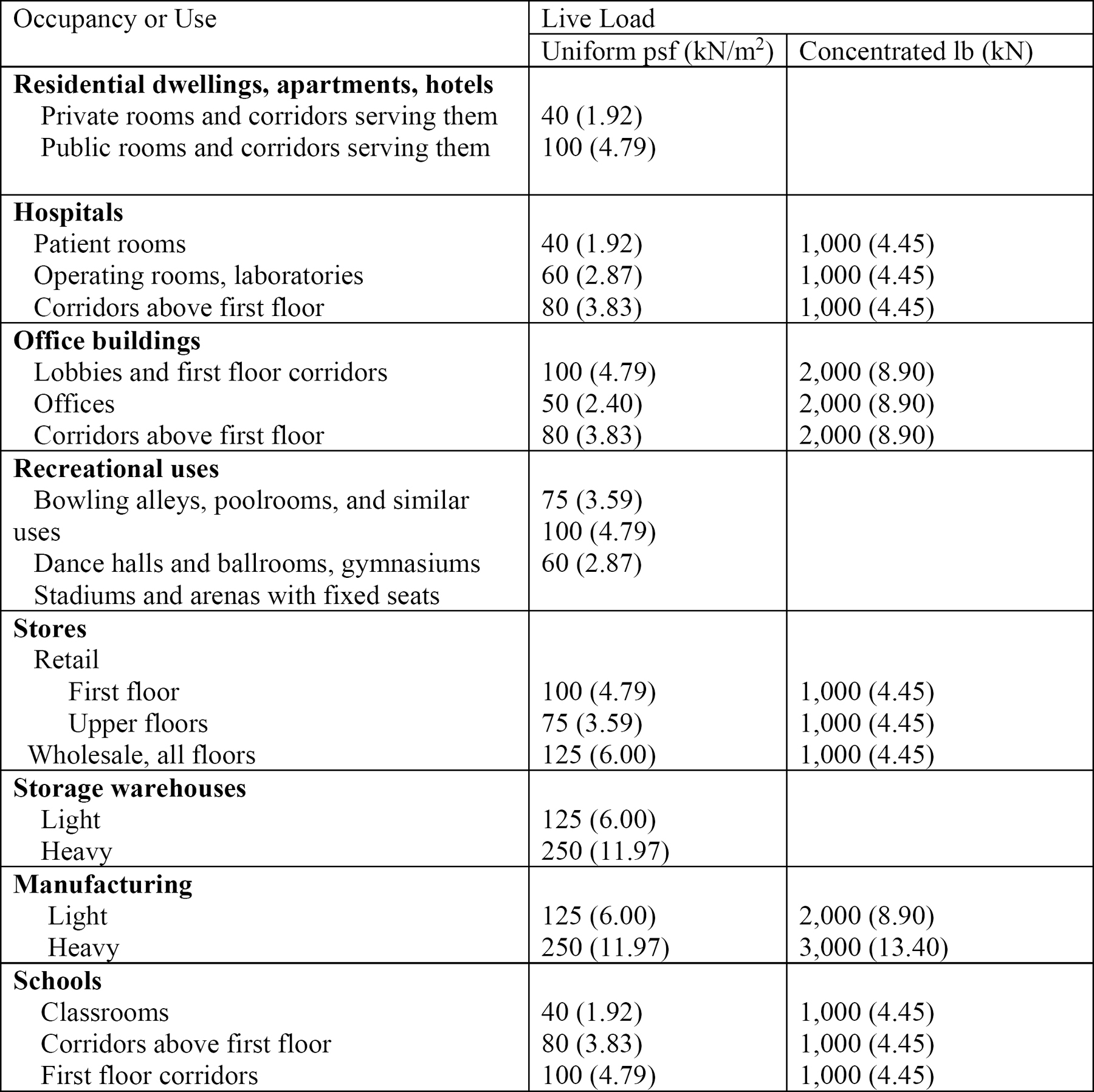
Loads on buildings and structures 2 1 introduction 2 1 1 scope this chapter specifies the minimum design forces including dead load live load wind and earthquake loads miscellaneous loads and their various combinations.
For standing seam and through fastened metal panel.
2attic loads may be included in the floor live load but a 10 psf attic load is typically used only to size ceiling joists adequately for access purposes.
Roofs are under a lot of pressure.
We will use a value between 1 5 and 2 5 to account for this extra stuff.
Table 3 2 2 summarizes the calculation.
D dead load l live load l r live roof load w wind load s snow load e earthquake load r rainwater load or ice water load t effect of material temperature h hydraulic loads from soil f hydraulic loads from fluids.
Roof live loads largest roof loads typically caused by repair and maintenance pitch rise span lr 20 r1r2 12 lr 20 lr horizontal projection roof live load 16 r 1 r 2 live load reduction factors r 1 accounts for size of tributary area of roof column a t r 2 effect of the roof rise.
Calculating the load on a flat roof is a challenging task for the layperson that involves knowledge of building materials their weights and local building codes.